Is a buccal pit a cavity? This question often arises when discussing oral health, as both buccal pits and cavities are common features found in the mouth. While they may share some similarities, understanding their distinct characteristics is crucial for maintaining optimal oral hygiene.
Buccal pits, natural anatomical depressions on the cheek side of the molars, are often mistaken for cavities. However, unlike cavities caused by tooth decay, buccal pits are harmless developmental variations that do not require treatment unless they become infected.
Definition of a Buccal Pit: Is A Buccal Pit A Cavity
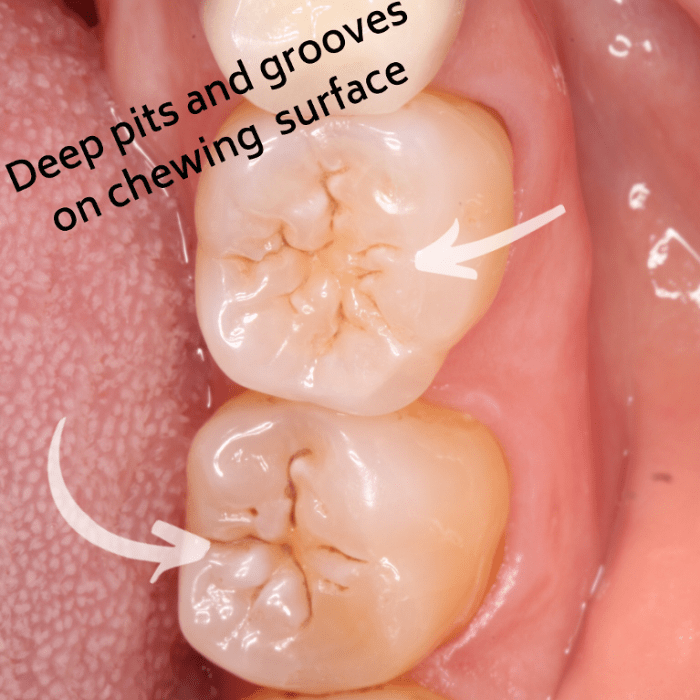
A buccal pit is a small, shallow depression located on the outer surface (buccal surface) of a tooth, most commonly found on molars and premolars. It is a developmental groove or indentation in the enamel, the hard outer layer of the tooth.
Buccal pits are formed during tooth development when the enamel is still soft and pliable. As the tooth erupts into the mouth, the enamel hardens and the pits become permanent features of the tooth’s surface.
Developmental Process of Buccal Pits, Is a buccal pit a cavity
The development of buccal pits is a complex process that involves the interaction of several factors, including the genetics of the individual, the environment in which the tooth develops, and the overall health of the mother during pregnancy.
- Genetics:The shape and size of buccal pits are largely determined by genetics. Some individuals are more likely to have deep, well-defined buccal pits, while others may have shallow, barely noticeable pits.
- Environment:The environment in which the tooth develops can also affect the formation of buccal pits. For example, exposure to certain chemicals or toxins during pregnancy has been linked to an increased risk of developing deep buccal pits.
- Maternal health:The overall health of the mother during pregnancy can also play a role in the development of buccal pits. For example, mothers who are malnourished or who have certain medical conditions are more likely to give birth to children with deep buccal pits.
Buccal Pits vs. Cavities
Buccal pits and cavities, though related, are distinct entities with key differences. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for proper dental care and maintaining oral health.
Key Characteristics
- Definition:Buccal pits are natural depressions on the buccal (cheek) surface of molars, while cavities are areas of tooth decay caused by bacteria.
- Appearance:Buccal pits appear as small, shallow indentations, whereas cavities often have a darker color and rough texture due to enamel damage.
- Location:Buccal pits are typically found on the upper molars, while cavities can occur anywhere on the tooth.
- Formation:Buccal pits form during tooth development, while cavities result from the breakdown of tooth enamel by acids produced by bacteria.
- Treatment:Buccal pits do not typically require treatment unless they become infected, while cavities require prompt treatment to prevent further damage.
Potential for Buccal Pits to Develop into Cavities
While buccal pits are not inherently cavities, they can increase the risk of cavity formation. Bacteria and food particles can accumulate in these depressions, creating an environment conducive to decay. Proper oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, is essential for preventing buccal pits from developing into cavities.
Diagnosis and Treatment
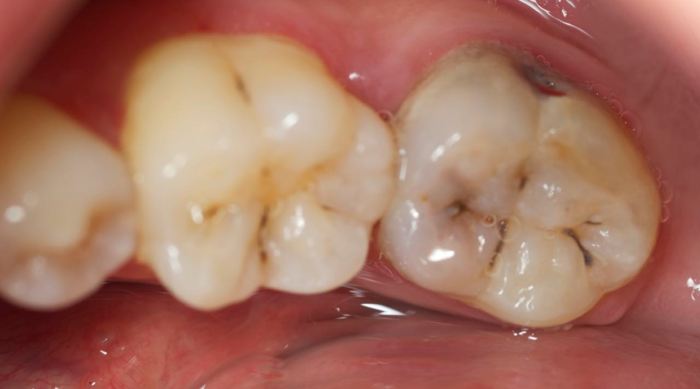
Diagnosis of buccal pits and cavities involves a thorough dental examination. The dentist will visually inspect the teeth, using a dental mirror and explorer to check for any visible signs of decay or developmental defects. Dental X-rays may also be taken to reveal any hidden cavities or other abnormalities.
Treatment for buccal pits and cavities varies depending on the severity of the condition. For small, non-cavitated buccal pits, the dentist may recommend regular monitoring and fluoride treatments to strengthen the enamel and prevent decay. If a cavity has formed, the dentist will typically remove the decayed tissue and restore the tooth with a filling.
Importance of Early Detection and Intervention
Early detection and intervention are crucial for preventing further damage to the tooth and surrounding tissues. Buccal pits, if left untreated, can develop into cavities, leading to pain, infection, and potentially tooth loss. Regular dental checkups and prompt treatment of any detected buccal pits or cavities can help preserve the health and longevity of the teeth.
Prevention and Management
Minimizing the risk of developing buccal pits and cavities involves adopting proactive measures. Proper oral hygiene practices and dietary choices play a crucial role in maintaining good oral health. Regular dental check-ups are equally important for early detection and prompt treatment of any dental issues.
Prevention begins with daily oral hygiene habits. Regular brushing with fluoride toothpaste helps remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth, including hard-to-reach areas like buccal pits. Flossing daily helps clean between teeth, removing food particles and bacteria that can lead to cavities.
Is a buccal pit a cavity? It’s a common question with a simple answer: no. A buccal pit is a harmless groove or depression in the cheek, while a cavity is a hole in the tooth caused by decay. To learn more about music theory, check out the g major scale 2 octaves . It’s a great way to expand your musical knowledge and improve your playing skills.
So, if you’re curious about buccal pits, rest assured that they’re nothing to worry about. But if you’re concerned about a cavity, be sure to see your dentist for a checkup.
Dietary Choices
Limiting sugary foods and drinks is essential. These foods create an acidic environment in the mouth, which can erode tooth enamel and increase the risk of cavities. Instead, opt for healthy snacks like fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are vital for maintaining oral health. During these appointments, your dentist can examine your teeth for any signs of buccal pits or cavities. Early detection allows for prompt treatment, preventing further damage and preserving your oral health.
Clinical Significance
Buccal pits and cavities pose significant clinical implications, influencing oral health and overall well-being. Understanding their clinical significance aids in appropriate management and preventive strategies.
Buccal pits, if left untreated, can progress into cavities, leading to discomfort, pain, and infection. Cavities in buccal pits are challenging to detect and restore due to their hidden location, often leading to extensive damage before detection.
Impact on Oral Health
Buccal cavities can contribute to tooth decay, pulpitis (inflammation of the tooth’s nerve), and even tooth loss if not addressed promptly. They act as reservoirs for bacteria and food debris, promoting plaque formation and acid production, which erodes tooth enamel.
Management in Different Patient Populations
Management of buccal pits and cavities varies based on the patient’s age, risk factors, and the extent of the condition. In children, sealants may be recommended to prevent pits from developing into cavities. For adults, regular dental check-ups and fluoride treatments are crucial for early detection and intervention.
FAQ Guide
What is the difference between a buccal pit and a cavity?
Buccal pits are natural depressions on the cheek side of the molars, while cavities are tooth decay caused by bacteria.
Can buccal pits develop into cavities?
Yes, if buccal pits are not properly cleaned and become infected, they can develop into cavities.
How can I prevent cavities?
Regular brushing, flossing, limiting sugary foods, and visiting the dentist for checkups can help prevent cavities.