Pathway for oxygenation crossword clue – Embark on a journey through the pathway for oxygenation, an intricate system that sustains life. From the lungs to the tissues, this article unravels the mechanisms of oxygen exchange, transport, and utilization, shedding light on the fundamental processes that keep us alive.
Beginning with the respiratory system, we delve into the vital role of the lungs in oxygenation. We explore the mechanisms of gas exchange in the alveoli, where oxygen is taken up and carbon dioxide is released.
Pathway for Oxygenation
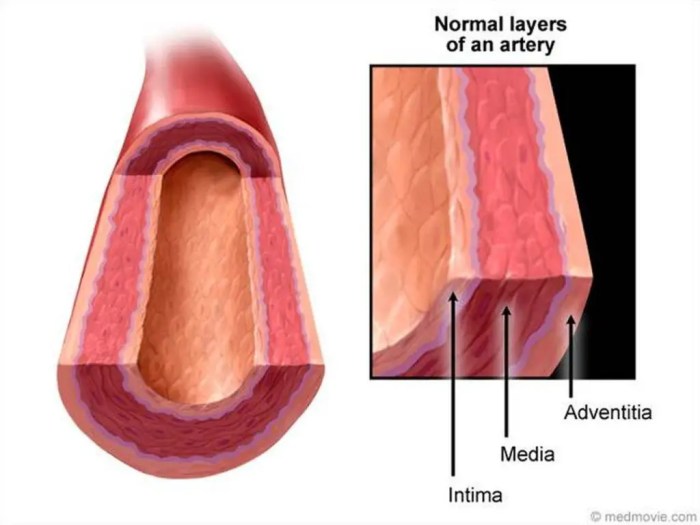
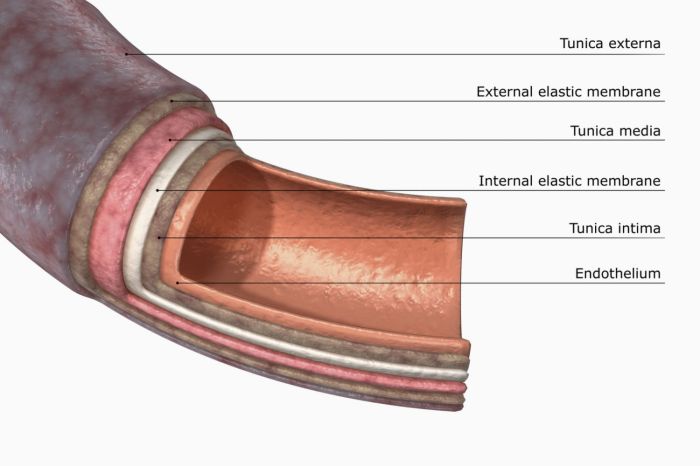
Oxygenation is a critical process for maintaining cellular function and overall health. The pathway of oxygenation involves a series of physiological mechanisms that facilitate the delivery and utilization of oxygen to tissues. This process encompasses several key stages, including respiration, oxygen transport, tissue oxygenation, and regulation of oxygenation.
Respiration
Respiration refers to the process of gas exchange between the body and the external environment. The respiratory system, primarily comprising the lungs, plays a central role in oxygenation. During respiration, inhaled air enters the lungs, where oxygen is transferred from the alveoli to the bloodstream.
Simultaneously, carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular respiration, is removed from the bloodstream and exhaled.The alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs that provide a large surface area for gas exchange. Oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses across the thin alveolar walls and into the capillaries surrounding the alveoli.
Hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells, binds to oxygen and transports it throughout the body.
Oxygen Transport
Oxygenated blood is pumped from the lungs by the heart and circulated through the arteries to the tissues. Hemoglobin plays a crucial role in oxygen transport, as it has a high affinity for oxygen and binds to it reversibly. As blood flows through the capillaries in the tissues, oxygen dissociates from hemoglobin and diffuses into the surrounding interstitial fluid.The
delivery of oxygen to tissues is influenced by several factors, including blood flow, hemoglobin concentration, and the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. Adequate blood flow is essential for ensuring a sufficient supply of oxygen to tissues. Hemoglobin concentration affects the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood, and a low hemoglobin level (anemia) can impair oxygen delivery.
The affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen can be affected by factors such as pH and temperature, which can influence the release of oxygen from hemoglobin.
Tissue Oxygenation, Pathway for oxygenation crossword clue
Once oxygen is delivered to the tissues, it is utilized by cells for energy production through cellular respiration. The mitochondria, organelles within cells, are responsible for oxidative phosphorylation, the process by which oxygen is used to generate ATP, the primary energy currency of cells.Tissue
oxygenation is influenced by factors such as the rate of cellular metabolism, oxygen consumption, and the diffusion distance between capillaries and cells. Cells with high metabolic rates require more oxygen, and impaired diffusion can limit oxygen availability to tissues.
Regulation of Oxygenation
The body has elaborate mechanisms to regulate oxygenation and maintain homeostasis. The respiratory center in the brain, primarily located in the medulla oblongata, controls breathing rate and depth. Chemoreceptors in the body, such as the carotid bodies and aortic bodies, sense changes in oxygen levels and blood pH and send signals to the respiratory center to adjust breathing accordingly.The
regulation of oxygenation involves feedback mechanisms that maintain optimal oxygen levels. When oxygen levels fall, the respiratory center increases breathing rate and depth to enhance oxygen intake. Conversely, when oxygen levels rise, the respiratory center decreases breathing to prevent excessive oxygenation.
Clinical Significance
Impairments in oxygenation can lead to a range of clinical conditions. Hypoxia, a deficiency of oxygen supply to tissues, can result from various factors, such as respiratory disorders, anemia, or cardiovascular disease. Hyperoxia, an excess of oxygen supply, can also occur in certain situations, such as during oxygen therapy or at high altitudes.The
assessment of oxygenation involves diagnostic tests such as arterial blood gas analysis, pulse oximetry, and capnography. These tests provide information about oxygen levels, carbon dioxide levels, and blood pH, helping clinicians evaluate oxygenation status and identify potential abnormalities.Treatment strategies for improving oxygenation vary depending on the underlying cause.
Oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, and blood transfusions are common interventions used to manage conditions that impair oxygenation. Understanding the pathway of oxygenation is essential for diagnosing and managing these conditions effectively.
Key Questions Answered: Pathway For Oxygenation Crossword Clue
What is the role of hemoglobin in oxygen transport?
Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that binds to oxygen molecules and transports them from the lungs to the tissues.
What factors can affect oxygen delivery to tissues?
Factors that can affect oxygen delivery to tissues include blood flow, hemoglobin concentration, and the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.