As we delve into the realm of label the tissue types illustrated here, we embark on a captivating journey into the microscopic realm. This comprehensive exploration unveils the intricacies of diverse tissue types, their defining characteristics, and their pivotal roles in shaping organ function and overall health.
Through the lens of histological staining techniques, we unravel the secrets of cellular components and structures. We trace the hierarchical organization of tissues, from their fundamental building blocks to the intricate tapestry of organs and systems. By examining tissue pathology, we gain invaluable insights into disease diagnosis and the potential of tissue engineering in regenerative medicine.
Tissue Types Illustrated: Label The Tissue Types Illustrated Here
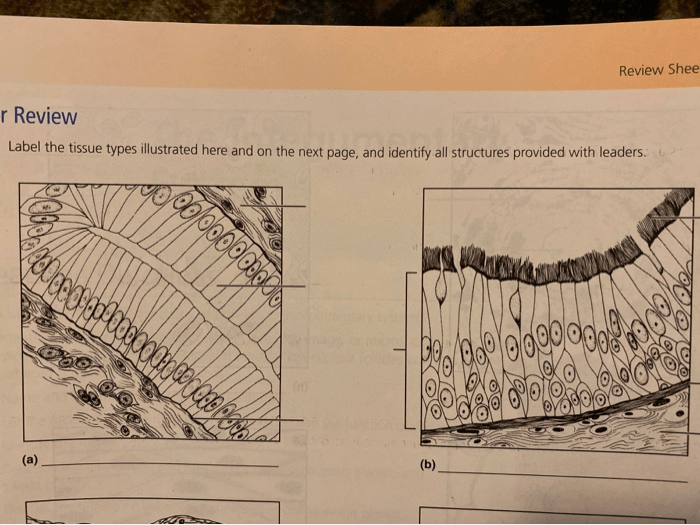
Tissues are organized groups of cells that perform specific functions. The different tissue types can be classified based on their structure and function. This article provides an overview of the different tissue types visible in the provided illustrations, explaining their characteristics and functions.
Epithelial Tissue
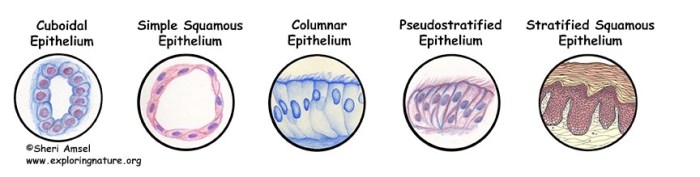
Epithelial tissue forms the lining of organs and cavities throughout the body. It protects underlying tissues from damage and provides a barrier against infection. Epithelial tissue can be classified based on the shape of its cells and the number of cell layers present.
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue supports and connects other tissues and organs. It consists of cells embedded in a matrix of extracellular material. The different types of connective tissue include loose connective tissue, dense connective tissue, cartilage, and bone.
Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue is responsible for movement. It consists of cells that contain specialized proteins that allow them to contract. The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.
Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is responsible for transmitting information throughout the body. It consists of neurons, which are specialized cells that transmit electrical signals, and glial cells, which support and protect the neurons.
Histological Staining
Histological staining techniques are used to differentiate between different tissue types and to highlight specific cellular components or structures. The most common histological staining techniques include:
Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining, Label the tissue types illustrated here
H&E staining is a routine histological staining technique that uses hematoxylin to stain the nuclei of cells blue and eosin to stain the cytoplasm pink. This technique provides a basic overview of tissue structure.
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry uses antibodies to bind to specific proteins within cells. This technique allows researchers to identify and localize specific proteins within tissues.
In Situ Hybridization
In situ hybridization uses probes to bind to specific DNA or RNA sequences within cells. This technique allows researchers to identify and localize specific genes within tissues.
Tissue Organization
Tissues are organized into organs, which are groups of tissues that perform a specific function. Organs are further organized into systems, which are groups of organs that work together to perform a complex function.
Hierarchical Organization of Tissues
The hierarchical organization of tissues can be represented as follows:
- Cells
- Tissues
- Organs
- Systems
Interactions of Different Tissue Types
The different tissue types interact with each other to contribute to organ function. For example, epithelial tissue lines the organs and provides a barrier against infection, while connective tissue supports and connects the different tissues and organs.
Tissue Pathology
Tissue analysis can be used to identify and diagnose disease. Tissue biopsies are samples of tissue that are removed from the body and examined under a microscope. Biopsies can be used to diagnose a variety of diseases, including cancer, infections, and autoimmune disorders.
Role of Tissue Biopsies in Medical Diagnostics
Tissue biopsies play a critical role in medical diagnostics. They allow doctors to examine the tissue under a microscope and identify any abnormalities that may be indicative of disease. Biopsies can also be used to determine the stage of a disease and to guide treatment decisions.
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering is the process of creating functional tissues and organs from living cells. Tissue engineering has the potential to revolutionize medicine by providing new treatments for a variety of diseases and injuries.
Principles of Tissue Engineering
The principles of tissue engineering involve:
- Isolation of cells from the patient
- Culture of cells in the laboratory
- Creation of a scaffold to support the cells
- Implantation of the engineered tissue into the patient
Challenges and Limitations of Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering faces a number of challenges and limitations, including:
- The need for a suitable cell source
- The difficulty of creating a scaffold that is compatible with the body
- The risk of infection and rejection
FAQ Guide
What are the different types of tissue?
There are four main types of tissue: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue.
How are tissue types identified?
Tissue types are identified based on their structure, function, and location in the body.
What is the role of histological staining in tissue identification?
Histological staining techniques highlight specific cellular components or structures, allowing for the differentiation between different tissue types.