How were the unifications of Italy and Germany similar? This question delves into a captivating historical comparison, shedding light on the intriguing parallels between these two significant events. By examining the political, economic, and social factors that shaped the unification movements in both countries, we gain a deeper understanding of the complexities and shared experiences that defined this transformative era.
The unifications of Italy and Germany were characterized by a shared desire for national unity and independence. Both countries faced internal divisions and external pressures, and both experienced the rise of nationalism as a driving force behind their unification movements.
Economic factors, such as industrialization and trade, also played a significant role in shaping the unification process.
Historical Context

Before unification, Italy and Germany were fragmented into numerous independent states. In Italy, the dominant powers were the Kingdom of Sardinia and the Papal States. In Germany, the Austrian Empire and Prussia competed for control.
Key figures in the unification process included Giuseppe Garibaldi and Camillo Benso di Cavour in Italy, and Otto von Bismarck in Germany. Movements such as the Risorgimento in Italy and the German Confederation played significant roles.
Methods of Unification

Italy and Germany employed different strategies to achieve unification. Italy relied on diplomatic alliances and military campaigns, such as the Thousand Expedition and the Second Italian War of Independence.
Germany, under Bismarck’s leadership, pursued a policy of “blood and iron,” using diplomacy, alliances, and three wars (the Danish-Prussian War, the Austro-Prussian War, and the Franco-Prussian War) to unify the German states.
Role of Nationalism
Nationalism played a pivotal role in both Italian and German unification. Patriotic sentiments and the desire for national identity fueled the unification movements.
In Italy, the Risorgimento emphasized the idea of a unified Italian state, while in Germany, the German Confederation sought to promote a sense of national unity.
Economic Factors
Economic factors also influenced the unification process. Industrialization and trade contributed to economic growth and a desire for a larger internal market.
In Germany, the Zollverein, a customs union, promoted economic cooperation among German states and facilitated the unification process.
International Influences: How Were The Unifications Of Italy And Germany Similar
Foreign powers played a role in the unification of Italy and Germany. France supported Italian unification, while Austria opposed it.
In Germany, the influence of Russia and France was significant, as Bismarck played them against each other to secure German interests.
Challenges and Obstacles
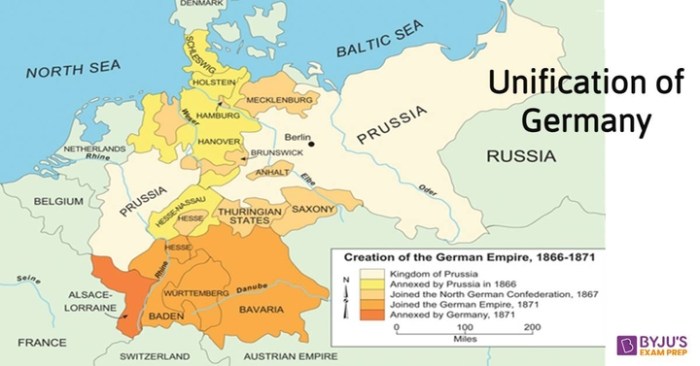
The unification process faced numerous challenges. In Italy, internal divisions and external pressures from Austria hindered unification.
In Germany, Prussia’s dominance and resistance from southern German states presented obstacles that Bismarck had to overcome through diplomacy and military force.
Outcomes and Legacies

The unification of Italy and Germany had significant outcomes. In Italy, it led to the creation of a unified kingdom and a period of economic and social progress.
In Germany, unification resulted in the establishment of the German Empire and its emergence as a major European power. The unification movements had a lasting impact on the political, economic, and social development of both countries.
FAQ Guide
What were the key similarities between the unifications of Italy and Germany?
Both unifications were driven by nationalism, economic factors, and the desire for national unity and independence.
How did nationalism contribute to the unification movements in Italy and Germany?
Nationalism provided a sense of shared identity and purpose, motivating people to work towards a common goal of unification.
What were the major challenges faced by Italy and Germany during the unification process?
Both countries faced internal divisions, external pressures, and economic challenges that hindered the unification process.