Initial concentrations of conjugates in buffer solutions play a pivotal role in establishing and maintaining chemical equilibria, influencing the behavior and properties of these essential chemical systems. Understanding their impact is crucial for various applications, ranging from biological processes to industrial chemistry.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the significance of initial conjugate concentrations, exploring the factors that govern their values and the experimental methods employed to determine them. We also uncover their diverse applications and highlight areas for future research and development.
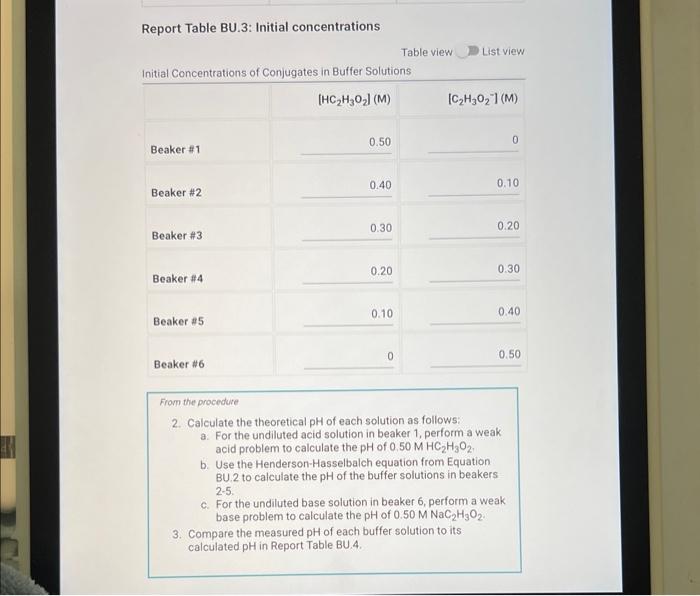
Initial Concentrations of Conjugates in Buffer Solutions

Initial concentrations of conjugates in buffer solutions refer to the starting concentrations of the conjugate acid and conjugate base present in a buffer system.
The initial concentrations of conjugates play a crucial role in determining the buffer’s capacity to resist changes in pH upon the addition of acids or bases.
Factors Affecting Initial Concentrations
- Dissociation constant (Ka or Kb) of the weak acid or base:A higher dissociation constant indicates a weaker acid or base, resulting in higher initial concentrations of conjugates.
- Desired pH of the buffer:The initial concentrations of conjugates can be adjusted to achieve a specific pH by manipulating the ratio of weak acid to conjugate base or vice versa.
- Concentration of the weak acid or base:Increasing the concentration of the weak acid or base will also increase the initial concentrations of conjugates.
Experimental Methods, Initial concentrations of conjugates in buffer solutions
| Method | Steps |
|---|---|
| pH Measurement |
|
| Conductivity Measurement |
|
Applications
- pH control in biological systems:Buffers are essential for maintaining the optimal pH for enzymatic reactions and other biochemical processes.
- Analytical chemistry:Buffers are used to control pH in titrations and other analytical procedures.
- Industrial processes:Buffers are employed in various industrial applications, such as electroplating and food preservation.
Limitations and Future Directions
Current methods for determining initial concentrations of conjugates have limitations, including accuracy and sensitivity.
Future research will focus on developing more precise and reliable methods for measuring initial concentrations of conjugates, as well as exploring novel applications in various fields.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the significance of initial conjugate concentrations in buffer solutions?
Initial conjugate concentrations determine the buffer capacity and pH stability of the solution, making them crucial for controlling chemical reactions and maintaining optimal conditions for biological processes.
How do factors such as temperature and ionic strength affect initial conjugate concentrations?
Temperature changes alter the equilibrium constant, thereby influencing the initial conjugate concentrations. Ionic strength affects the activity coefficients of ions, which in turn impact the equilibrium concentrations.
What experimental methods are commonly used to determine initial conjugate concentrations?
Spectrophotometry, pH measurements, and potentiometric titrations are widely employed to quantify initial conjugate concentrations accurately.