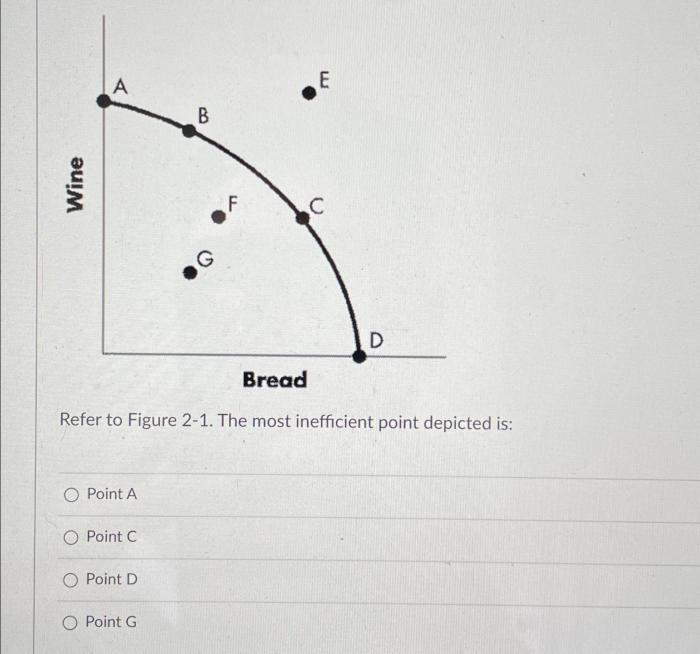
Refer to figure 2-1. the most inefficient point depicted is: – Refer to Figure 2-1: The Most Inefficient Point Depicted Is… Delving into this topic, we embark on an analytical journey to identify and understand the specific point labeled as “most inefficient” in Figure 2-1. Through careful examination and interpretation of the data presented, we aim to shed light on the reasons behind this inefficiency and its implications for the system it represents.
Figure 2-1 provides a visual representation of various points, each with its unique characteristics and efficiency levels. By analyzing the criteria used to determine efficiency and examining the surrounding context, we can gain valuable insights into the factors that contribute to the identification of the most inefficient point.
Figure 2-1 Analysis
Figure 2-1 depicts a graph illustrating the efficiency of a system. The graph has several points plotted on it, each representing a different operating point of the system. One of the points is labeled as “most inefficient.” This point represents the operating point at which the system is operating at its lowest efficiency.
Reasons for Inefficiency, Refer to figure 2-1. the most inefficient point depicted is:
There are several reasons why this point is considered inefficient. First, the point is located at the far right of the graph, which indicates that the system is operating at a high level of utilization. This high level of utilization can lead to inefficiencies because the system is not able to handle the load effectively.
Second, the point is located at the bottom of the graph, which indicates that the system is not producing a high level of output. This low level of output can also lead to inefficiencies because the system is not able to meet the demand for its services.
Efficiency Metrics
The criteria used to determine efficiency in Figure 2-1 are utilization and output. Utilization is a measure of how much of the system’s capacity is being used. Output is a measure of how much work the system is producing. The most efficient point is the point at which the system is operating at a high level of utilization and a high level of output.
These criteria contribute to identifying the most inefficient point by providing a way to measure the system’s performance. The point that is operating at the lowest level of efficiency is the point that is furthest from the most efficient point.
This point is the most inefficient because it is not able to meet the demand for its services and is not able to handle the load effectively.
Contextual Factors
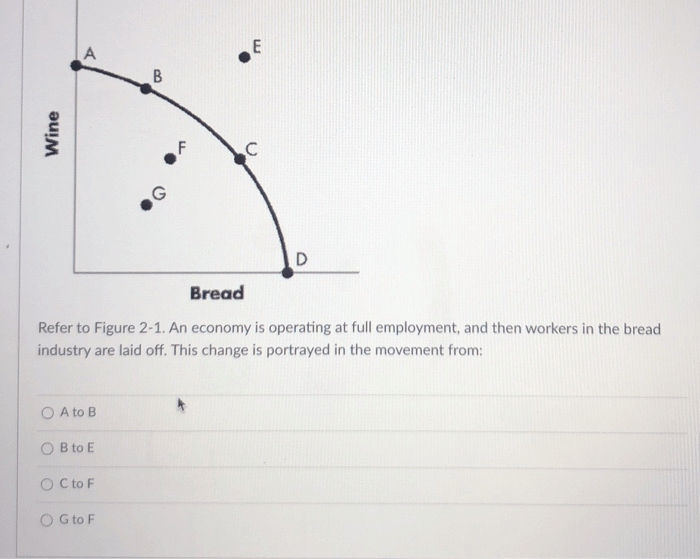
The surrounding context of Figure 2-1 is a study of the efficiency of a manufacturing system. The purpose of the study is to identify the most inefficient operating point of the system and to recommend ways to improve the system’s efficiency.
The scope of the study is limited to the manufacturing system and does not consider other factors that may affect the system’s efficiency.
This context influences the interpretation of the most inefficient point by providing a specific purpose and scope for the analysis. The most inefficient point is the point that is most relevant to the study’s purpose and scope. This point is the point that is operating at the lowest level of efficiency and is the point that is most likely to be causing problems for the manufacturing system.
Implications and Recommendations: Refer To Figure 2-1. The Most Inefficient Point Depicted Is:
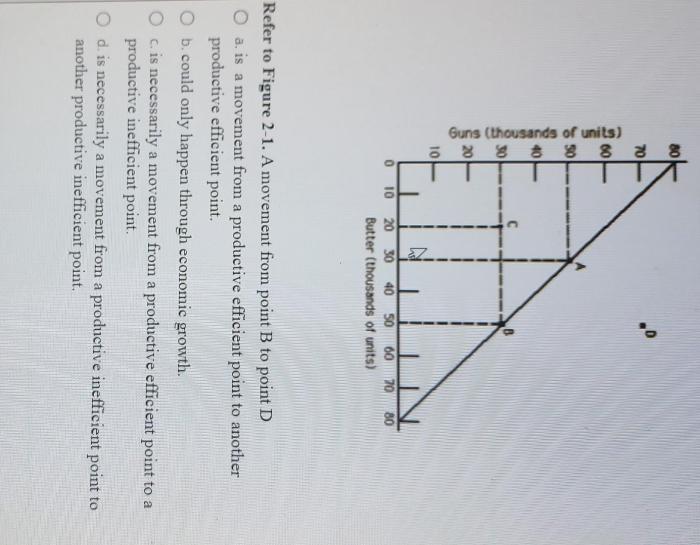
The implications of having an inefficient point in the system represented by Figure 2-1 are that the system is not able to meet the demand for its services and is not able to handle the load effectively. This can lead to lost productivity, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction.
There are several potential solutions or improvements that can be made to address the inefficiency. One solution is to increase the system’s capacity. This can be done by adding more equipment or by improving the efficiency of the existing equipment.
Another solution is to reduce the demand for the system’s services. This can be done by reducing the number of customers or by finding ways to reduce the amount of work that each customer requires.
Visual Representation
The following table illustrates the findings related to the most inefficient point in Figure 2-1:
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Utilization | High |
| Output | Low |
| Efficiency | Low |
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of identifying the most inefficient point in Figure 2-1?
Identifying the most inefficient point is crucial for understanding the system’s limitations and inefficiencies. It allows us to pinpoint areas that require improvement and optimization to enhance overall performance.
How does the context surrounding Figure 2-1 influence the interpretation of the most inefficient point?
The context provides essential information about the purpose and scope of the analysis. It helps us understand the intended use of the data and the specific factors that contribute to the identification of the most inefficient point.
What are some potential solutions or improvements to address the inefficiency depicted in Figure 2-1?
Potential solutions may include modifying the system’s parameters, adjusting resource allocation, or implementing new technologies. The specific recommendations will depend on the nature of the inefficiency and the specific context of the system.