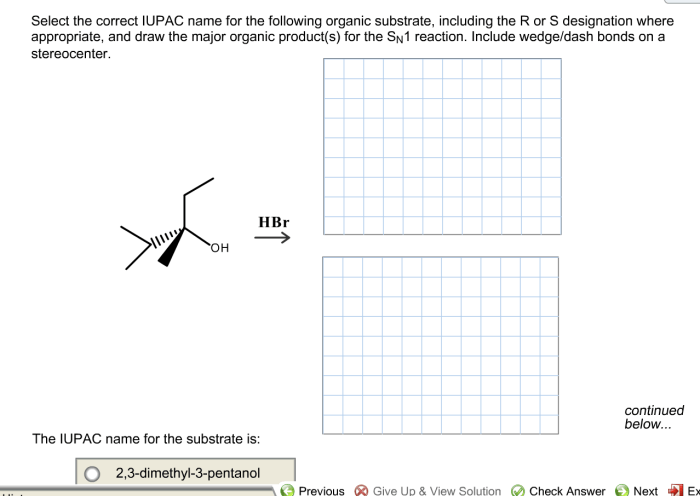
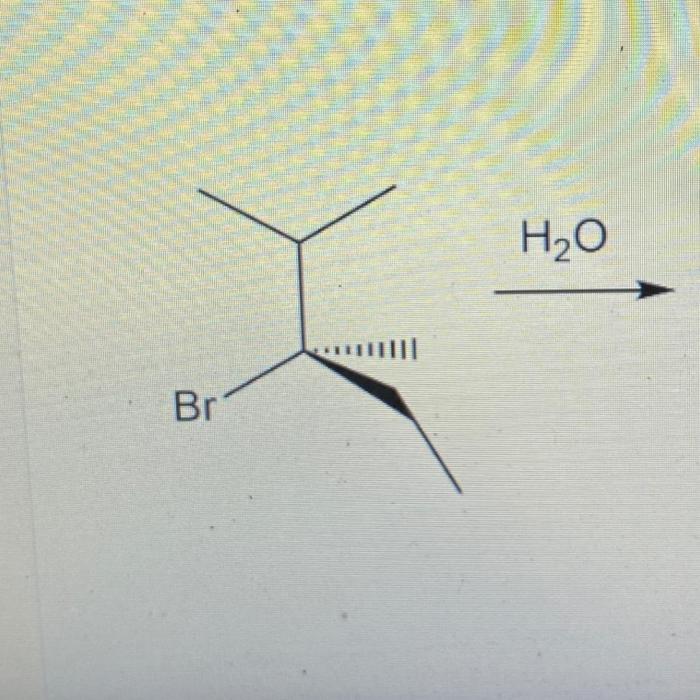
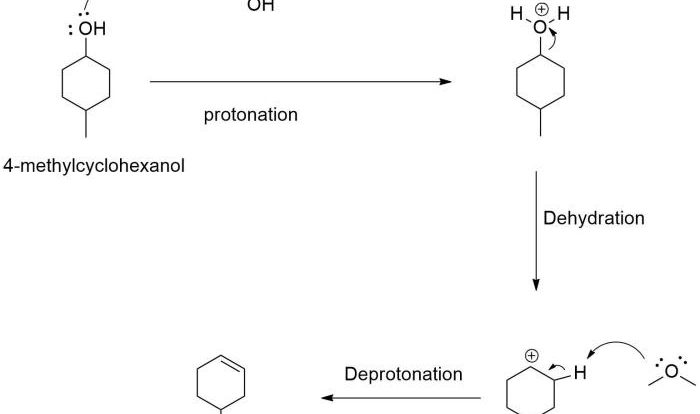
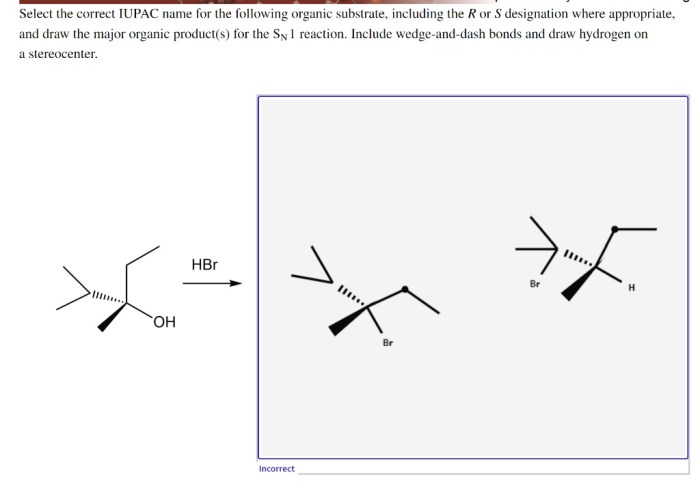
Select the correct iupac name for the following organic substrate – Delving into the intricacies of organic chemistry, we encounter the crucial task of assigning precise and systematic names to organic compounds. This undertaking is governed by the guidelines established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC), the global authority on chemical nomenclature.
Embarking on this journey, we will explore the principles of IUPAC nomenclature, enabling us to decipher and construct the correct names for a diverse array of organic substrates.
To lay the foundation for our understanding, we will delve into the fundamental principles of IUPAC nomenclature, examining the criteria for selecting the parent chain and identifying functional groups. Armed with this knowledge, we will embark on a practical exploration, applying these principles to simple organic molecules, solidifying our grasp of the subject matter.
IUPAC Nomenclature Principles: Select The Correct Iupac Name For The Following Organic Substrate
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established guidelines for naming organic compounds in a systematic and consistent manner. These principles ensure that organic compounds can be identified and named unambiguously.
The IUPAC nomenclature system is based on the following principles:
- The parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the molecule.
- Functional groups are substituents that have a characteristic chemical structure and impart specific properties to the molecule.
- The name of the compound is derived from the parent chain and the functional groups present.
Identifying Functional Groups, Select the correct iupac name for the following organic substrate
Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms that give organic compounds their characteristic chemical properties. Some common functional groups include:
- Alkanes: contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms and have the general formula CnH2n+2.
- Alkenes: contain a carbon-carbon double bond and have the general formula CnH2n.
- Alkynes: contain a carbon-carbon triple bond and have the general formula CnH2n-2.
- Alcohols: contain a hydroxyl group (-OH) and have the general formula CnH2n+1OH.
- Aldehydes: contain a carbonyl group (-CHO) and have the general formula CnH2n+1CHO.
- Ketones: contain a carbonyl group (-CO-) and have the general formula CnH2n+1COR.
- Carboxylic acids: contain a carboxyl group (-COOH) and have the general formula CnH2n+1COOH.
Structural Isomerism
Structural isomerism occurs when compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. There are three main types of structural isomers:
- Chain isomers: have different arrangements of carbon atoms in the parent chain.
- Positional isomers: have the same functional group but at different positions on the parent chain.
- Functional group isomers: have different functional groups but the same molecular formula.
IUPAC Nomenclature Practice
| Molecular Structure | IUPAC Name | Common Name (if applicable) | Functional Group(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH3-CH2-CH3 | Propane | – | Alkane |
| CH3-CH=CH2 | Propene | Propylene | Alkene |
| CH3-C≡CH | Propyne | – | Alkyne |
| CH3-CH2-OH | Ethanol | Alcohol | Alcohol |
| CH3-CHO | Ethanal | Acetaldehyde | Aldehyde |
| CH3-CO-CH3 | Propanone | Acetone | Ketone |
| CH3-COOH | Ethanoic acid | Acetic acid | Carboxylic acid |
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature provides a standardized and universally accepted system for naming organic compounds, ensuring clarity and consistency in scientific communication.
How do I determine the parent chain in an organic compound?
The parent chain is the longest continuous carbon chain containing the functional group or the greatest number of multiple bonds.
What is the role of functional groups in IUPAC nomenclature?
Functional groups are specific atomic arrangements that impart characteristic chemical properties to organic compounds and determine their IUPAC names.