Embarking on an exploration of bisectors in triangles quiz part 1, we delve into the captivating realm of geometry, where angle bisectors play a pivotal role. These geometric entities, defined as the rays that divide angles into two equal parts, hold significant properties and applications that we will uncover throughout this engaging discourse.
As we progress, we will encounter the Angle Bisector Theorem, unravel its converse, and delve into the intricate web of theorems and properties that govern angle bisectors in triangles. Along the way, we will witness their practical applications in real-world scenarios, problem-solving, and the art of construction and design.
Angle Bisectors in Triangles: Bisectors In Triangles Quiz Part 1
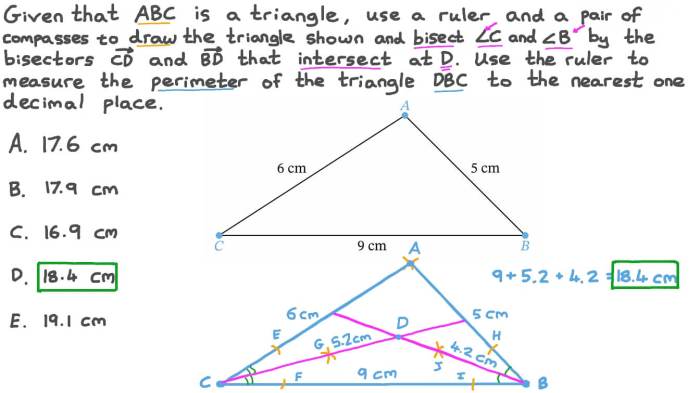
In geometry, an angle bisector is a line or ray that divides an angle into two equal parts. Angle bisectors play a crucial role in triangle geometry and have numerous applications in solving geometry problems.
Definitions and Concepts, Bisectors in triangles quiz part 1
An angle bisector is a ray that originates from the vertex of an angle and divides it into two equal angles. The angle bisector of an angle ∠ABC is denoted by BD, where B is the vertex and BD divides ∠ABC into two equal angles, ∠ABD and ∠CBD.
Angle bisectors possess several important properties. For instance, the angle bisector of an angle in a triangle divides the opposite side into segments proportional to the adjacent sides. Additionally, the angle bisectors of a triangle intersect at a single point, known as the incenter.
Theorems and Properties
The Angle Bisector Theorem states that in a triangle, the ratio of the lengths of the segments of the opposite side formed by an angle bisector is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the adjacent sides. This theorem provides a powerful tool for solving geometry problems involving triangles.
The converse of the Angle Bisector Theorem also holds true. If the ratio of the segments of the opposite side formed by a line is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the adjacent sides, then the line is an angle bisector.
Applications
Angle bisectors have practical applications in various fields. In construction and design, angle bisectors are used to create symmetrical designs and divide angles accurately. In surveying, angle bisectors are employed to determine the direction of lines and boundaries.
Angle bisectors also play a crucial role in solving geometry problems. They can be used to find the measure of angles, determine the lengths of sides, and construct congruent triangles.
Advanced Concepts
The concept of angle bisectors extends to more advanced topics in geometry. Angle bisectors are closely related to concurrency theorems, which describe the intersection points of various lines in a triangle.
Angle bisectors also have applications in advanced geometry topics such as cyclic quadrilaterals, where they are used to construct and analyze inscribed and circumscribed circles.
FAQ Summary
What is the definition of an angle bisector?
An angle bisector is a ray that divides an angle into two equal parts, creating two congruent angles.
State the Angle Bisector Theorem.
The Angle Bisector Theorem states that in a triangle, the ratio of the lengths of the two sides that form the angle is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the segments of the third side created by the angle bisector.
What is the converse of the Angle Bisector Theorem?
The converse of the Angle Bisector Theorem states that if the ratio of the lengths of the two sides of a triangle that form an angle is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the segments of the third side created by a ray, then that ray is the angle bisector.